One of the things that worries me most when teaching vocabulary is that students tend to store the newly acquired knowledge as passive vocabulary. Agreed that most of us have more passive than active vocabulary, agreed that we use a larger variety of words when we write than when we speak, but still I think that as teachers we need to go the extra mile and help our students see the importance of incorporating new vocabulary into their communicative tasks.
Designing activities to convert passive vocabulary into active vocabulary is one of the things that occupies most of my planning.

This is a very simple activity I have designed to” force” my students to use new vocabulary and connectors to express contrast.
Level : Intermediate and above
Aim:
- To use newly acquired vocabulary
- To improve students’ writing abilities by using connectors of contrast
- To encourage collaborative writing
Step 1. Selecting vocabulary. Ask students to work in pairs. Explain that they’ll need to write on a clean sheet of paper ten words or expressions recently studied. (You can also be more specific here and tell them the unit or the pages of the book you want them to get the vocabulary from).
Step 2. Explaining the task .Ask students now to pass their list of 1o words to the pair sitting behind them or next to them.
Tell students they are going to write a story in pairs. In this story they’ll need to use at least 7 of the words on their list and three out of the five connectors of contrast you are going to write on the board (see below an interactive flyer explaining Clauses of Contrast)
Give them the beginning of a story, for example “When Fiona entered the room, she couldn’t believe her eyes” or use a story starter generator here.
Step 3. Writing and editing. Encourage students to dedicate some time to planning their story. Set a time limit of 30 minutes, but I suggest not limiting the number of words in their stories to encourage fluency and boost their imagination.
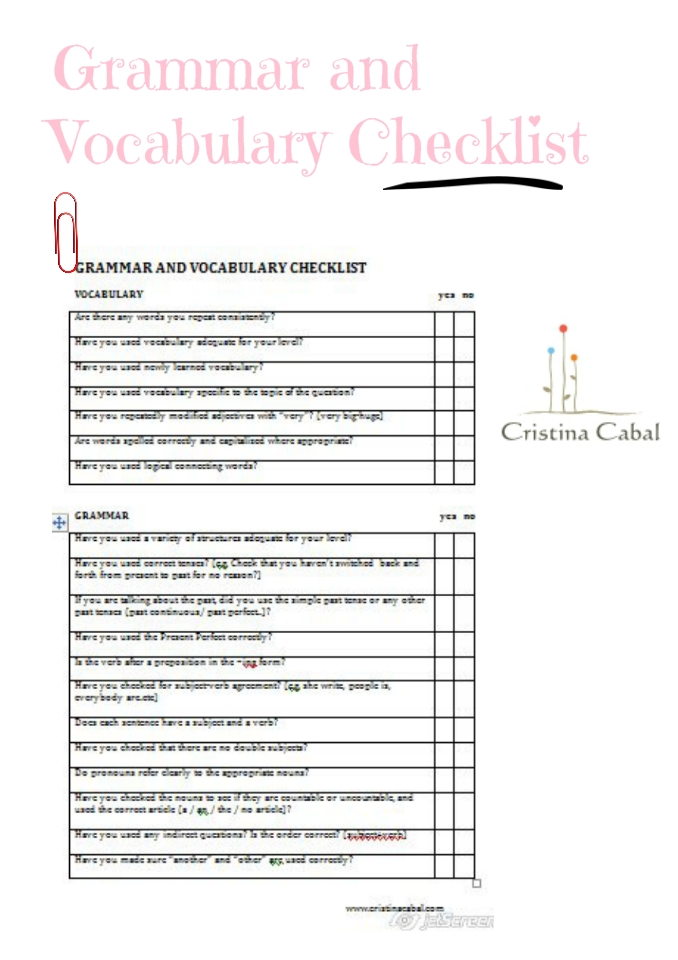
Once they have written their draft (20 minutes), ask students to carefully edit their stories. Display the following checklist on the board (click here to download it) or alternatively print it and give one to every student.
Give each pair a different coloured paper or if you have more stories than colours, use different pen colours or assign a number to every story.
Ask students to write their story and underline the targeted vocabulary and the connectors of contrast used.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Clauses of Contrast Flyer
Photo credit: Deb Stgo via Visual hunt / CC BY